Spiral Screwdrivers of Decatur, Illinois
Clifford D. Fales
The availability of better woodscrews and the rise of the factory system in the last quarter of the nineteenth century saw a proliferation of patents for more efficient tools for driving screws. Isaac Allard's spiral screwdriver patent of 1868 began a succession of some fifty spiral screwdriver patents before 1900. Additional patents for ratchet screwdrivers and screwholding screwdrivers give an indication of the demand for this type of tool. Decatur, Illinois was a location which was prominent in the development of these tools during this period of time.
The Decatur Coffin Company spiral screwdrivers and the often-told story about undertakers needing only a clockwise screwdriver are both familiar to many tool collectors. However, there is more to the Decatur story than this one frequently seen spiral screwdriver and the story commonly associated with it.
Christopher H. Olson
While only the patent date of October 7, 1884 is usually seen
on the Decatur Coffin Co. screwdrivers, C. H. Olson, the patent holder,
actually held four patents for spiral screwdrivers.
The most prevalent model, marked DECATUR COFFIN COMPANY / DECATUR, ILL'S / PAT. OCT. 7, 1884, is actually based on the third of four spiral screwdriver patents granted to Christoph
er H. Olson of Decatur (Figure 1) . It is most commonly seen in the 12" size but also is seen in a smaller 8" size. This model will also be observed with at least three different handle styles (Figures 2A, 2B, 3B & 4. Advertising and catalog illustrations designated this screwdriver variously as the Olson patent, The Eureka Screwdriver or The Decatur Coffin Company Screwdriver. While it is known that C. H. Olson was a member of the Board of Directors of the Decatur Coffin Company,1 the fact that he invented and perfected this screwdriver would seem to indicate that he also was significantly involved in the production processes in the factory
 |
 |
 |
|
A significant feature of the construction of this spiral screwdriver which sets it apart from all but a few other designs is the fact that the shaft derives its rotary motion from grooves cut on the inside of the tube into which the shaft telescopes, rather than machined in the shaft as is the case with most spiral screwdrivers.
Olson's October, 1884 patent was only the fifth for a spiral screwdriver which provided a mechanical means to allow the bit to remain in a stationary position while the handle is withdrawn for the next driving stroke. Others most notably the A. H. Reid patent number 268,938 of December 12, 1882 had some provision for this purpose but it was not an automatic mechanical release and required an adjustment of hand position or release of a lock for the return stroke. The Allard/Howard based on the Isaac Allard's patent number 157,087 of November 24, 1874 and the Decatur Coffin based on Olson's October, 1884 patent were apparently the first spiral screwdrivers using a mechanical release to gain widespread acceptance.
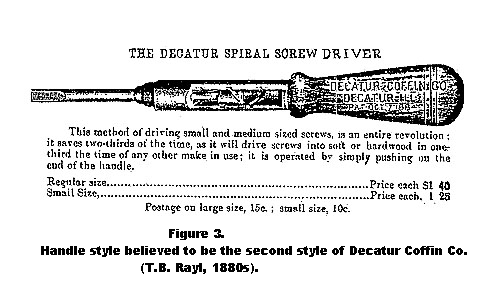
A warning to collectors: Many handles seen on the Decatur Coffin Co. screwdrivers are not original. A wide variety of owner-made, retro-fitted handles will be found. Although three original Decatur Coffin Co. handle styles are identified here, there are others which have strong indications of also being original. This is a subject which will benefit from further study.
Olson's First Patent
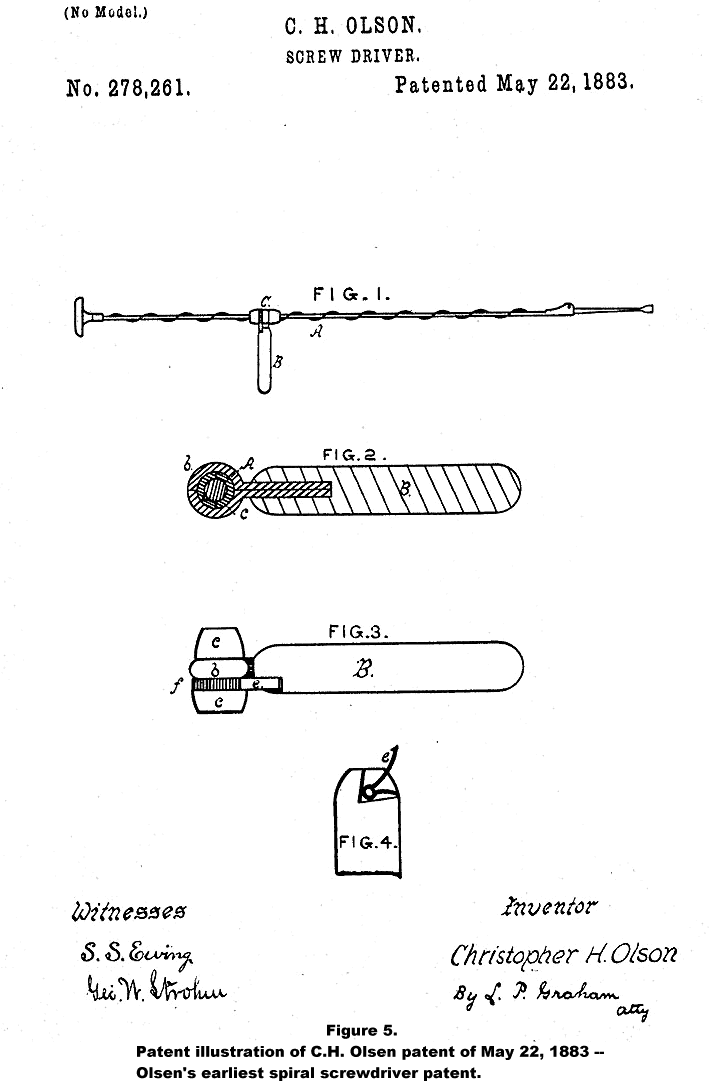
The first spiral screwdriver patent of C. H. Olson was number 278,261 granted on May 22, 1883 (Figure 5). The patent illustration shows a tool which would have been unusually long and unwieldy to use. Judging by the relationship of the size of the slide handle and bit to the length of the entire tool, this tool would in all likelihood have been over thirty inches in length. The patent text indicates that one stroke normally is sufficient to drive a screw with this tool. This model has not been observed and it is certainly doubtful if it was produced commercially.
Olson's Bi-Directional Patent
Probably the most interesting part of this story is that Olson's second patent number 301,915, granted on July 15, 1884 — was for a bi-directional, reversible model (Figure 6). As far as I have been able to determine, this is the earliest patent for a bi-directional spiral screwdriver with the capability of both driving and removing screws by utilizing the reciprocating motion of the handle. Some earlier models did permit counter-clockwise rotation for removal of screws. This was done either by withdrawing the handle with a pulling motion or by means of locking the shaft to the handle and using a rotary motion, as with a standard non-spiral screwdriver. Open for speculation would be reasons why this bi-directional model, which would have had much more usefulness than a right-hand-only model, was not put into production and marketed. Surprisingly, Olson's October 1884 patent for the popular, heavily advertised model came only three months after this patent for the reversible model. I have seen no examples of this model. My supposition is that Mr. Olson did not have sufficient confidence in the design of the bi-directional model and moved ahead to production and marketing of the better designed uni-directional model.
Olson's 1889 Patent
Olson's final patent (Figure 7) shows a right-hand-only model with a square twisted shaft and with a removable, inter-changeable bit. Several features of this design seem to be for purposes of reducing manufacturing costs, i.e., substitution of a twisted shaft for a machined shaft and substitution of a combined wood handle/tube for the usual metal body tube. This model has not been observed.
Even though the Decatur Coffin Co. was an undertakers' supply house, it is obvious they marketed their screwdriver to the mechanic and carpenter trade. There were numerous advertisements in builders publications and listings in general tool catalogs for this tool during the 1890-1905 era. This brings up the question for tool collectors; did a manufacturer of undertakers' supplies make any tools other than this screwdriver?
O. Z. Greene
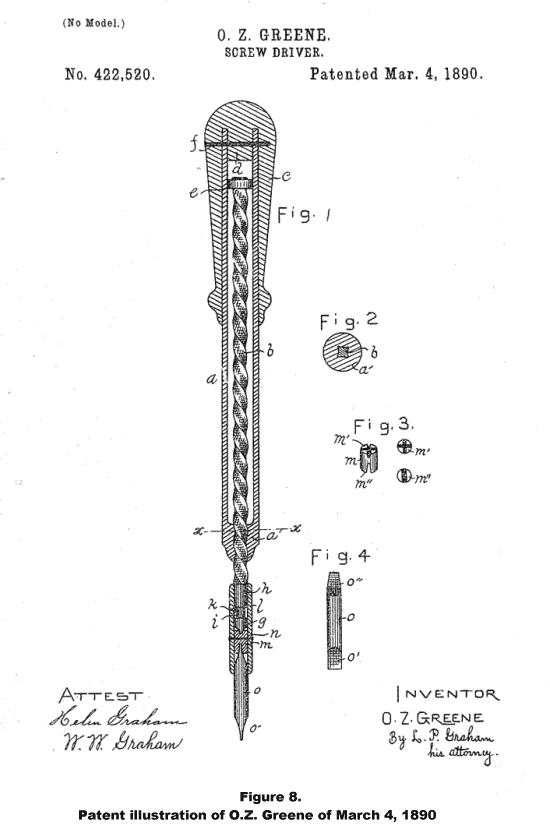
O. Z. Greene, president of The Decatur Coffin Co.2 also held a spiral screwdriver patent (Figure 8), but it apparently was never marketed.
H. Mueller Manufacturing Co.
The Decatur Coffin Company, C. H. Olson and O. Z. Greene, however, were not the only players in town. Decatur, Illinois, was also represented by at least one other manufacturer of spiral screwdrivers at the turn of the century. The H. Mueller Manufacturing Co., of Decatur, produced at least two models from the 1890's to at least 1913.3
Anton Schuermann Patent and the H. Mueller Screwdrivers
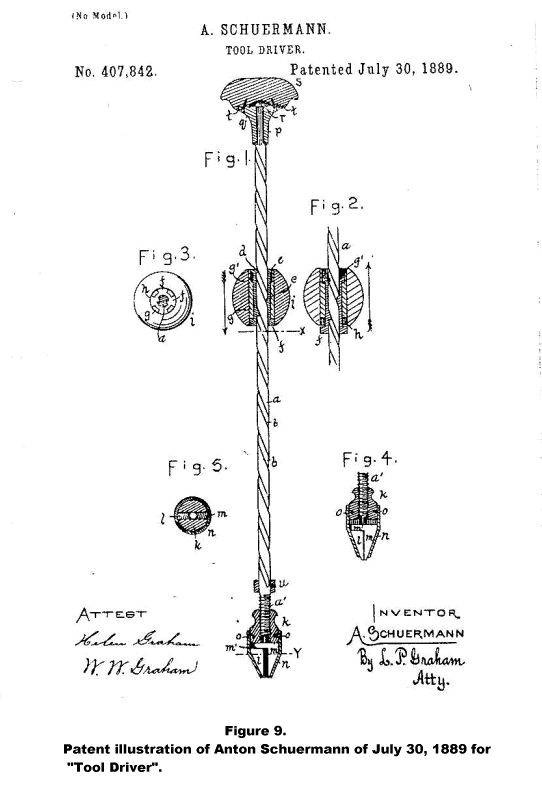
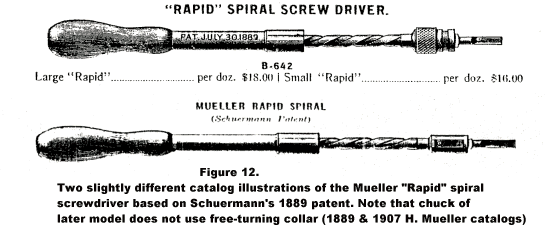
Anton Schuermann, an employee of H. Mueller Mfg. Co., was granted a patent for a "Tool Driver" (Figure 9) on July 30, 1889. It is illustrated in H. Mueller catalogs from 1899-1913 with a drill chuck (Figure 10)4 and in the October 1892 CARPENTRY & BUILDING with screwdriver chuck and bit4 (Figure 11A). I have observed only one actual example of this model of the Schuermann patent (Figure 11B). It is marked: H. Mueller Mfg. Co. / Decatur, Ill. / PAT. JULY 30, 1889. Another Mueller product, designated as the "Mueller Rapid" (Figure 12) shows little visual relationship to the above patent, but is based on the same patent. Examples are marked with the 1889 patent date and the catalog illustrations are marked with the date and labeled as "Schuermann Patent." The Mueller Rapid is frequently seen.
  |

 |
  |
The Mueller Co., now a subsidiary of the Grinnell Co., is still in business in Decatur. An officer has reported that there was no known relationship between the H. Mueller Manufacturing Co. and the Decatur Coffin Co.6 However, there is some evidence in the patents to indicate that there may have been some connection between the two firms. Not only did Olson and Schuermann engage the same attorney for the patent application process, but they used some of the same persons to witness their patent applications.
The Popular Story
This seems an appropriate time to refute the tale, popular among tool collectors, of the Decatur Coffin Company screwdriver being manufactured only in a right-hand, clockwise version for driving screws because the undertaker only needed to drive screws and had no need to remove them.
This does make a whimsical story; but, in truth, there was not a bi-directional spiral screwdriver available in the 1880's.7 The first bi-directional models, which did not appear in advertising and catalogs until the 1890s, were the Jones Reversible Spiral Screwdriver (1892 patent) appearing in 1897, the Forest City Spiral Screwdriver (1895 patent) in 18968 and the Goodell Pratt No. 22 (1897 patent) in the same year.9
Further explanation for the development of this screwdriver might be that it came about as a production tool within the Decatur Coffin Co. because of the need for driving wood screws in the manufacture of wooden caskets. Did the Decatur Coffin Co. possibly enter the tool manufacturing business and offer their spiral screwdriver to the trade after finding they had a good thing in what they had developed for in-house use? This is known to have been the case with at least one other spiral screwdriver a model manufactured by the S. F. Bowser Co. of Ft. Wayne, IN.10
The author is continuing research on screwdrivers and will welcome related information about screwdrivers in members' collections, advertising material, catalog references or patents.
Grateful acknowledgement is made to the following individuals and organizations who supplied information used in the preparation of this article: Harold Barker; Decatur (Illinois) Public Library; Martin J. Donnelly; Carl E. Floren, Corporate Directory of Quality Improvement, Mueller Co.; Paul B. Kebabian; Macon County (Illinois) Historical Society; Alvin Sellens and William T. Wilkins.
-
Decatur City Directory, 1889
-
Past and Present of the City of Decatur and Macon County, Illinois, Chicago, 1903, p. 9; O. T. Bainton, ed.,, History of Macon CountyHistory of Macon County, Decatur, Macon County Historical Society, 1976, p. 122
-
Catalog B, 1899, p. 111; Catalog C, 1903, p. 49; Catalog D, 1907 p. 66; Catalog D, 1913, p. 67, (Trade Catalogs) H. Mueller Manufacturing Company, Decatur.
-
Catalog B, 1899, p. 111; Catalog C, 1903, p. 49; Catalog D, 1907 p. 66; Catalog D, 1913, p. 67, (Trade Catalogs) H. Mueller Manufacturing Company, Decatur.
-
"Mechanic's Screw and Tool Driver," Carpentry & Building, January 1892
-
Carl E. Floren, letter to the author, July 25, 1994
-
A Book of Tools, (Trade Catalog) Charles A. Strelinger & Co., Detroit, 1895, p. 504
-
Tools For All Trades, (Trade Catalog) Hammacher, Schlemmer & Co., New York, 1896, p. 155
-
Woodworkers' Tools, (Trade Catalog) Chas. A. Strelinger & Co., Detroit, 1897, p. 715
-
O. M. Ramsey, "A Bowser Screwdriver," The Gristmill, 6, 4, 1986, p.23
About the Author:
Cliff Fales is retired after a thirty year career as a public school instrumental music teacher. He also has had an active part-time career in orchestral string instrument repair. He currently serves as secretary of Rocky Mountain Tool Collectors and editor of their newsletter. After primarily collecting rules for twenty years Cliff has in recent years also concentrated on spiral screwdrivers. He has previously written in THE CHRONICLE on Wheeler, Madden & Clemson saws and prepared the 1988-1993 CHRONICLE Index and in THE GRISTMILL of M-WTCA on the Lemuel Hedge / Morton Clark rule joint, extra-thick rules and Allard/Howard/Jones spiral screwdrivers..
Return to Spiral Screwdriver Home Page
Return to Spiral Screwdriver Database Page
I would appreciate hearing from you via e-mail if you have one of these or any other unusual or early spiral screwdrivers.
Text and images: Copyright © Clifford Fales, All Rights Reserved.
